Positioning: Creating an image of your product in your target customer’s mind
Researching a market? Our free online course Introduction to Market Sizing offers a practical 30-minute primer on market research and calculating market size.
Positioning is an essential part of launching your product and company in the market. Positioning creates an image of your company’s product in the mind of your target customer. The term “positioning” should be viewed both as a verb and a noun.
As a verb, it can be defined as deploying a set of tools and processes used to influence and control the market’s perception of your product or company in relation to any competing alternatives. As a noun, it can be defined as an attribute or condition associated with your product.
Still, positioning is not what your company physically does to a product—it is what your company does to a target customer’s mind. It provides an effective answer to the question, “What do you do?” Keep in mind that the question has to be answered from the customer’s point of view and clearly state what the product does for the customer.
Customers develop opinions about companies and products. And the positioning of each in the mind of the customer always occurs in relation to the competition or the customer’s other alternatives (which may include doing nothing).
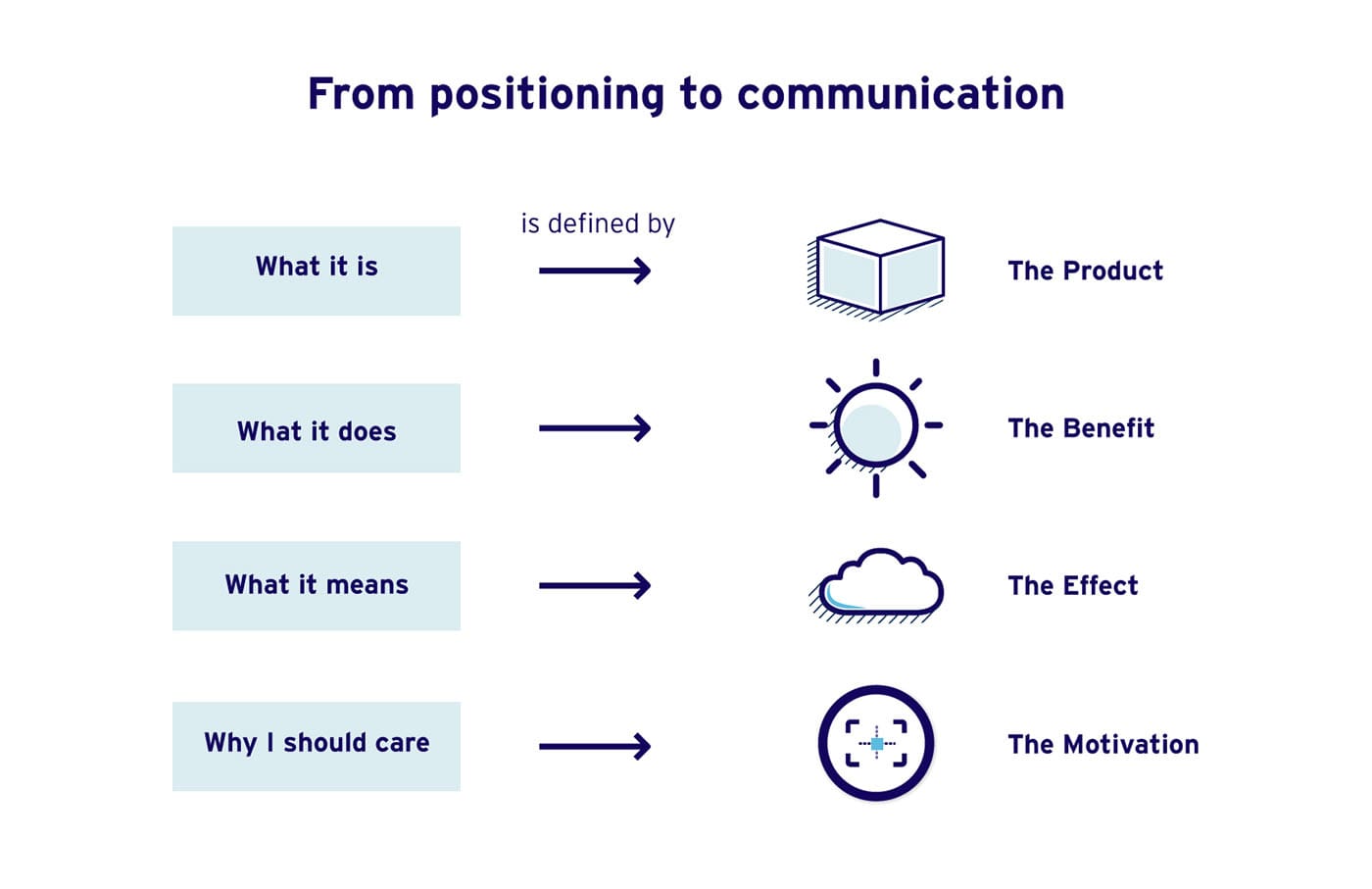

Positioning fundamentals
- Positioning is the single greatest influence on a customer’s buying decision
- Each customer evaluates products in the market according to their mental map of the market
- Positioning exists in customers’ minds, not in positioning statements
- People do not easily or willingly change their minds about a product’s positioning
- Positioning must first demonstrate a product’s relevance, using supportable, credible, and factual terms
- Making the product easier to buy through effective positioning makes the product easier to sell.
Mapping the market: Identifying and staking out target customer segments
Mapping the market involves identifying and staking out the most relevant customer segments. It enables you to establish and potentially control how your product is viewed in terms of benefit and differentiation.
Benefit: The advantage conveyed by the product to the target customer based on his compelling reason to buy.
Differentiation: The singling out of the one element that creates your benefit and makes you unique in the marketplace, at the same time bearing relevance to the customer.
Positioning template
The positioning template can help you to express the fundamental value proposition that your product provides to a target customer and the market. It must identify the:
- Target customer or market
- Compelling reason to buy
- Product’s placement within a new or existing category
- Key benefit that directly addresses the compelling reason to buy
- Primary alternative source (that is, competitor) of the same benefit
- Key difference or point of differentiation
Positioning statement
The positioning template enables you to create a positioning statement, which explains who you are, what you offer, whom it is for, and why it is important and compelling.
The positioning statement should meet several key criteria:
- It effectively identifies the target customer or segment, and makes the situation clear and understandable.
- It makes your claim (and related benefit) concise, singular and compelling and supports it by credible evidence.
- It makes the differentiation statement concise, singular, compelling, and supportable, and it reflects the target customer’s attributes and environment.
- It passes the “elevator test” (that is, it can be explained in a few words).
Using the template, a positioning statement can be structured like this:
- For (target customer or market)…
- Who (have a compelling reason to buy)….
- Our product is a (product’s placement within a new or existing category)….
- That provides (key benefit that directly addresses the compelling reason to buy)
- Unlike (primary alternative source [that is, competitor] of the same benefit)
- Our product (key difference or point of differentiation in relation to the specific target customer)
Positioning and market type
In a new market, you must define the market and your company’s place within it. This involves positioning your company to visionary buyers as a thought leader within an emerging, highly promising market category. You must also demonstrate your product’s benefit or competitive advantage against existing products and the status quo.
In an existing market, the positioning changes. Here, it must demonstrate to economic buyers and end-users that your product and application are the most credible and comprehensive option for the customers’ needs. In order to achieve the desired positioning, your communication must clearly articulate your unique points of differentiation.

